Ks means the actual number of synonymous substitutions that occurred at each possible synonymous site since the divergence of two sequences. The Ks distribution was used to reflect the evolutionary rates in different genomes and the timing of evolutionary events. We plotted the Ks distribution of syntenic homologous genes within the studied genomes and between C. chinensis and other genomes (Table S3 and Fig. 2, a). We found that the genes in different Ranunculales genomes evolved at divergent rates. The evolutionary rate of the C. chinensis genome (~0.9256 ±0.146) was the slowest in Ranunculales.
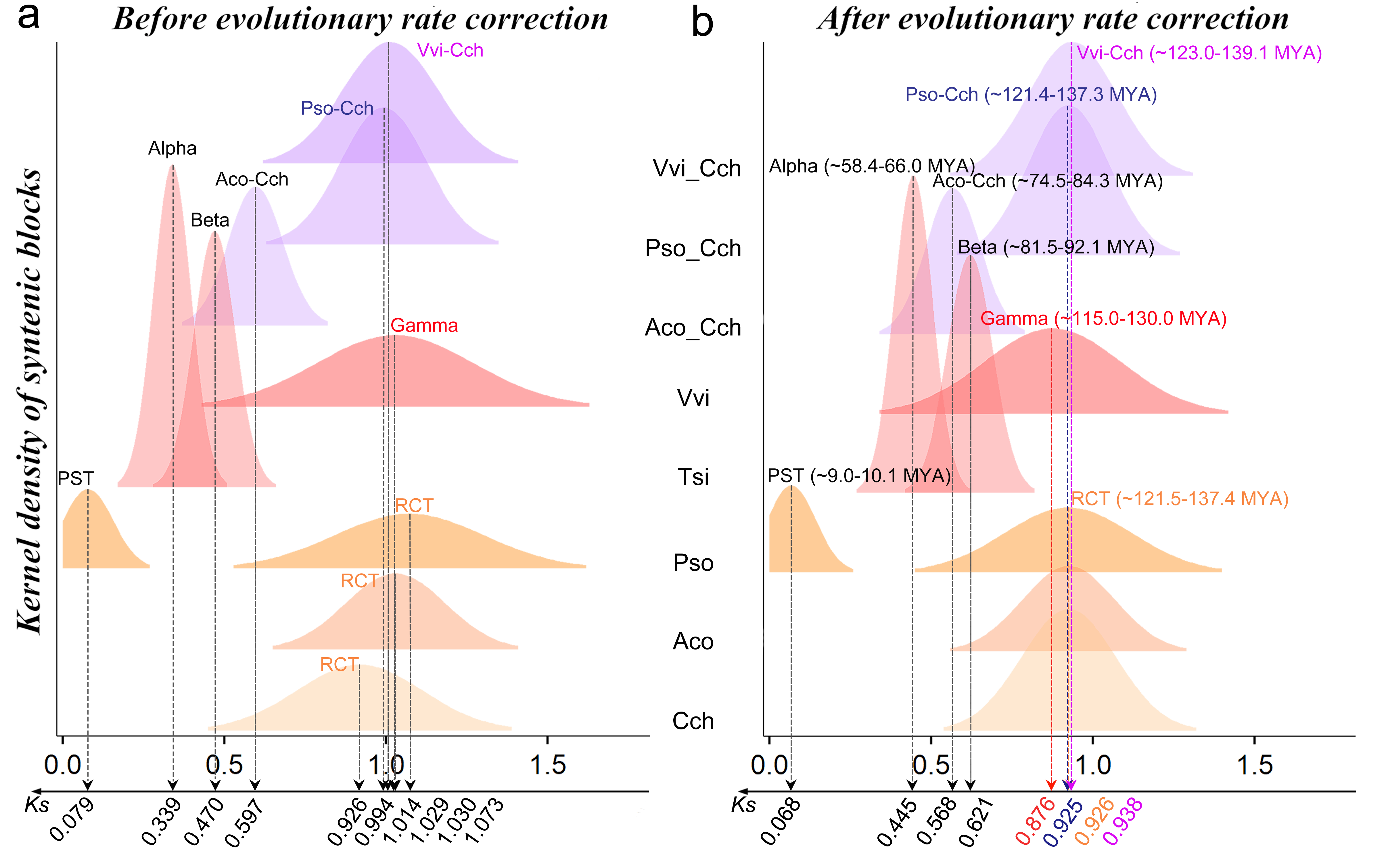
Original and corrected Ks distribution among syntenic genes within and between genomes of C. chinensis (Cch), A. coerulea (Aco), P. somniferum (Sievers et al.), T. sinense (Tsi) and V. vinifera (Vvi). (a) Distribution of Ks values between syntenic gene pairs before correction. (b) Distribution of Ks values among syntenic gene pairs after evolutionary rate correction. The different colored peaks indicate the normal distribution of the Ks values of syntenic genes.
