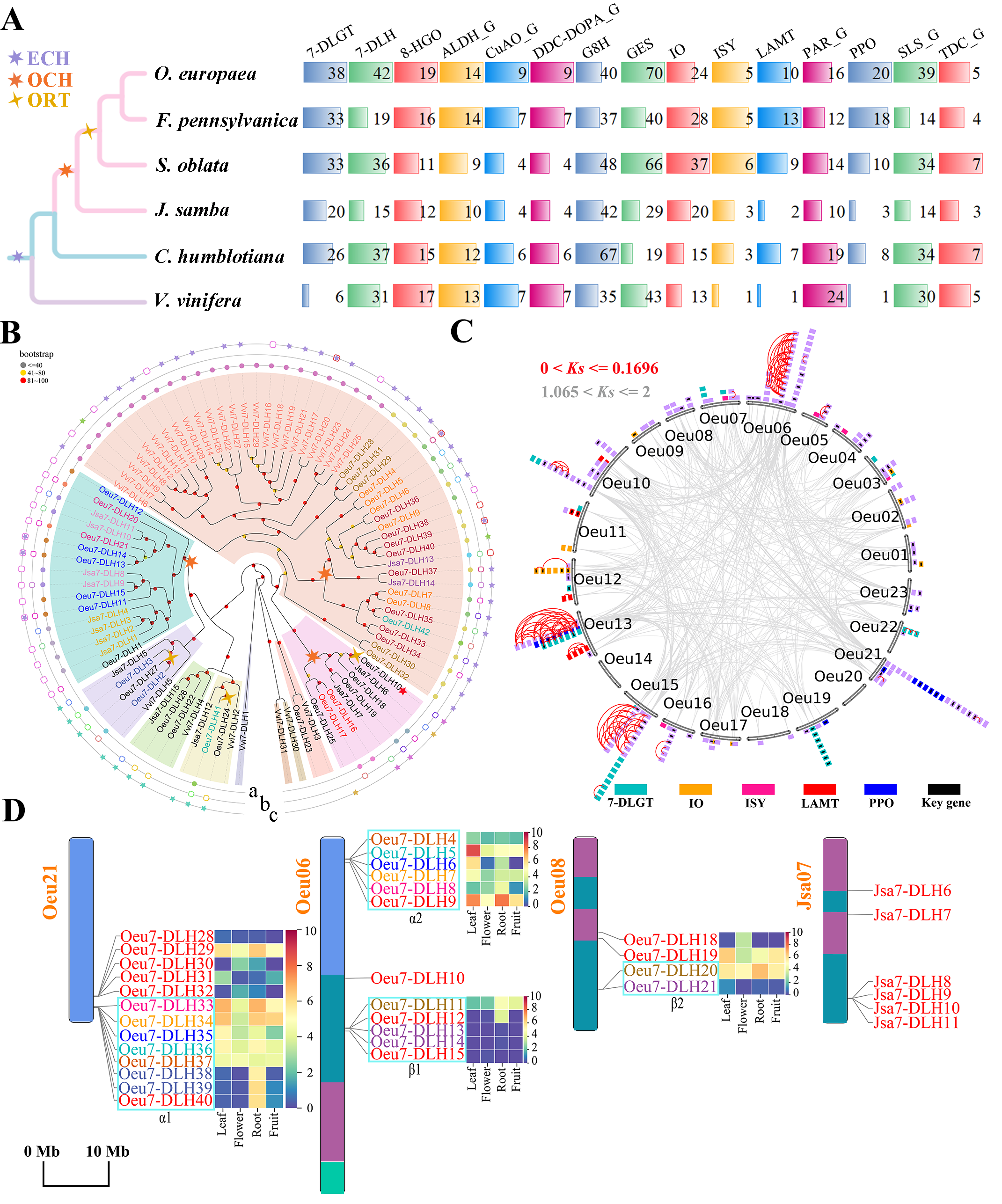
Evolution of OFAB gene families in the genomes of Oleaceae and outgroups. A, Identification of the OFAB gene families in the selected genomes. B, Phylogenetic tree of the 7-DLH genes from the genomes of J. sambac, O. europaea and V. vinifera. Genes from same cluster are marked with same color. Colored backgrounds are used to distinguish the orthologous gene groups across species. The dots on the three layers from inside to outside represent the tandem duplicated genes, paralogs, and orthologs, and the same color represents homologous relationships. The gene identified in previous study that can enhance the yield of oleuropein was labelled with red pentagram (Rodriguez-Lopez et al., 2021). C, The expansion pattern of gene families in O. europaea. Homologous gene pairs generated before the ECH event are linked with gray lines, and tandem duplicated gene pairs are linked with red lines. The color annotations of genes from the families (7-DLGT, IO, ISY, LAMT, and PPO) are located at the bottom, and the genes from other families denoted by purple. The key genes of oleuropein biosynthesis inferred from a previous study are marked in black (Rao et al., 2021). D, Chromosomal distribution of 7-DLH genes in O. europaea and J. sambac. The two sets of paralogous gene clusters associated with ORT event in O. europaea are α1 and α2, and β1 and β2, respectively. Among these four clusters, genes in different clusters with the same color represent ORT paralogs. Gene expression patterns were shown to the right of the genes. The chromosomes were color-coded with the ancestral Oleaceae karyotype.