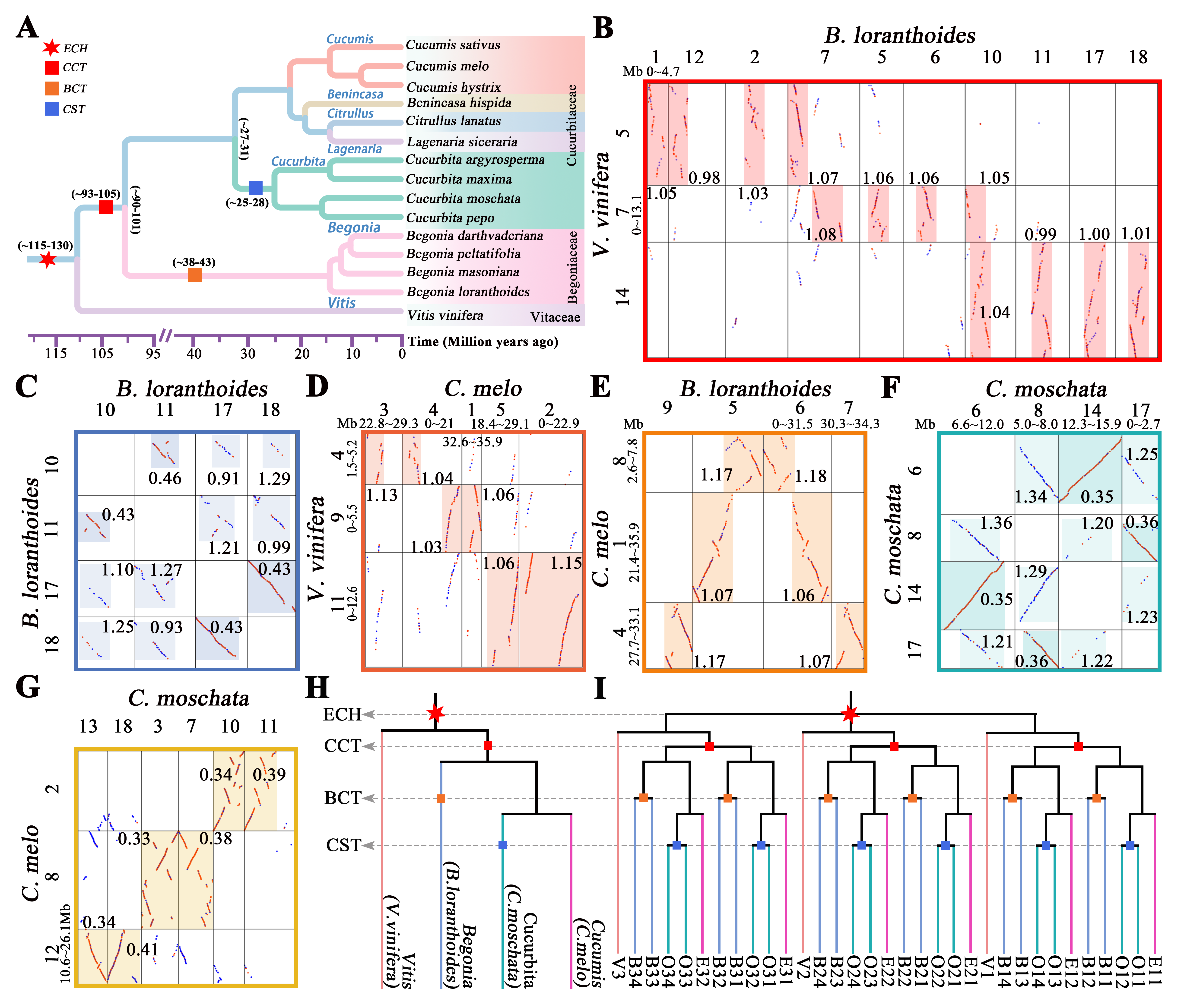
Intra/intergenomic homologous local dotplot, reveals that the Begoniaceae shared by common Paleotetraploidization with the Cucurbitaceae. (A) Phylogenetic relationships of the studied genomes in Cucurbitales. (B-G) Best-matched or homologous copies between or within V. vinifera, C. melo, C. moschata and B. loranthoides chromosomes. Best-hit genes are represented by red dots, other genes by gray dots. Highlighted areas of different brightness represent homologous regions. The Ks median of gene pairs in homologous chromosomal regions is marked near the blocks. The lengths of chromosomes are shown in Mb. (H) Species phylogenetic trees for the V. vinifera, C. melo, C. moschata and B. loranthoides chromosomes genomes. The red six-pointed star represent ECH events, and the red, orange and blue squares represent CCT, BCT and CST events, respectively. ECH, core-eudicot-common hexaploidization. CCT, Cucurbitales common tetraploidization, BCT, Begoniaceae common tetraploidization, CST, Cucurbita special tetraploidization. (I) Three ECH-produced paralogous genes in the V. vinifera (V) are denoted by V1, V2, and V3, each have four orthologs genes in B. loranthoides (B) or C. moschata (O) genomes and two in C. melo (E) genome.